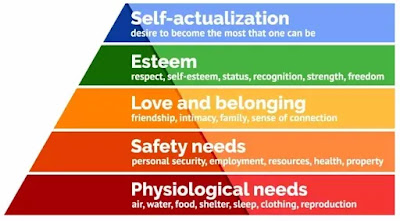
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory
in Psychology comprising of a five-tier model of human needs.
Physiological Needs – these are biological
requirements for human survival. For e.g. air, food, drink, shelter, clothing,
sex, sleep. If these needs are not satisfied the human body cannot function
optimally. These needs, according to Maslow, are the most important without
which other needs cannot be fulfilled.
Safety Needs – protection from elements, security,
order, law, stability, freedom from fear.
Love and Belonging Needs – The third level of
human needs is social and involves feelings of belonging. The need for
interpersonal relationships motivates behavior. E.g. Friendship, trust,
intimacy, etc.
Esteem Needs – are divided into two categories –
esteem fo oneself – dignity, achievement, independence; and the desire for
reputation or respect from others – status, prestige
Self-Actualization Needs – realizing personal
potential, self fulfillment, seeking personal growth and peak experiences.
CRITICISM
Maslow's model is a very popular model, but theoretically, there are a lot of loopholes.
The rigidity with which Maslow has sequenced theres needs. Critics have objected to the order of the needs. Though all needs are perceived, they don't have to be in the same order.
Accordint ot certain other critics, all needs given by Maslow may not be or perceive all needs. For e.g. some individuals will skip love and affection and go from safety to esteem.
There is no emperical evidence (observed cases) at all to substantiate this theory. According to critics, this theory is presented in a vaccume only to counter Freudian theory.
No comments:
Post a Comment