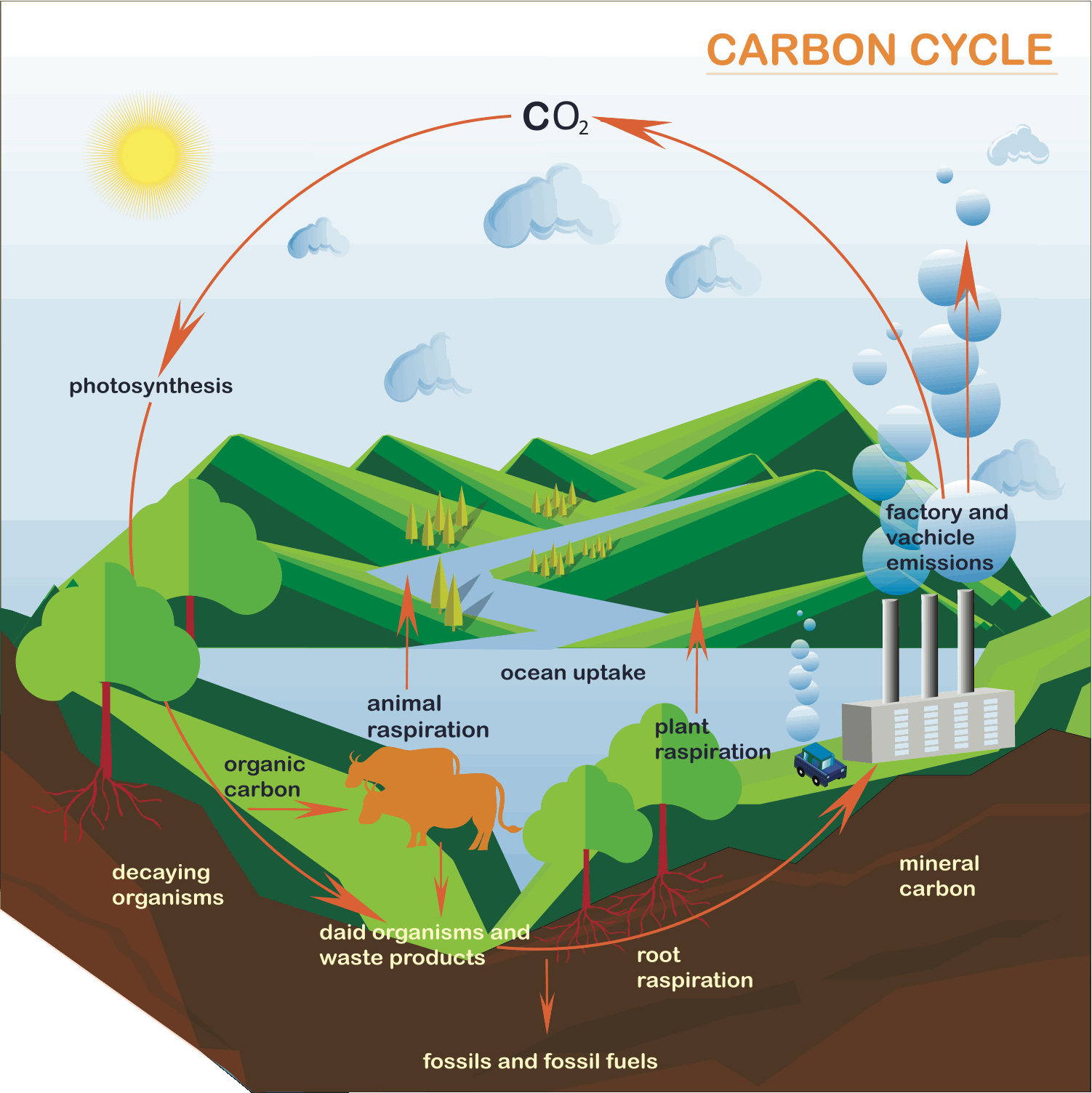
Carbon cycle involves movement of a chemical ‘carbon’ from the environment into living organisms and then back to environment.
The atmospheric CO2 enters the plants during photosynthesis
– the process by which plants prepare their own food in the presence of
sunlight. Carbon of the carbon dioxide gas is stored in the plant body while
oxygen is released back into the air.
The animals eat plants and hence carbon enters bodies of
animals. The carbon in animals is released back into the atmosphere as carbon
dioxide during respiration.
Sometimes plants are buried under the soil layers due to the
crustal movements and hence they get converted into coal due to heat and
pressure. When coal is extracted from the mine and burned in factories, carbon
in the coal combines with atmospheric oxygen and is released back to the
atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
Carbon is one of the most important gases in our atmosphere.
Earth needs carbon either for structure, energy or as in the case of humans,
for both.
Human activities such as burning of fossil fuels and
deforestation are responsible for the rapid increase in carbon dioxide
concentration leading to rise in atmospheric temperatures.
Higher concentrations of carbon dioxide and other green
house gases leads to increased trapping of infrared radiation. This results in
warming up of temperatures at lower levels, change in weather patterns and
climate.
Increased concentration of CO2 has an important impact on
plant growth – some plants respond more favorably to increase in CO2 than
others.
No comments:
Post a Comment